The Research and Graduate Networks are instances of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional that aim to promote and articulate the interrelation and research and professional cooperation between polytechnic teachers and researchers, promoting and consolidating the collective work of scientific and technological research, favoring the generation of frontier scientific knowledge, the development of cutting-edge technological tools, the gestation of evolutionary and disruptive innovations, and the search for adapted and effective solutions to regional, national and international problems, which have a positive social impact for society as a whole.
The vocation of the networks is to promote the cooperation and integration of the polytechnic community, as well as to create alliances and links with individuals and national and international entities, so that the results obtained could not be achieved without the active participation, openness of thought and the joint will of each and every one of the members of the networks, in their different scales and in their different forms.
On November 30, 2006, the Instituto Politécnico Nacional created the Nanoscience and Micro-nanotechnology, Biotechnology and Environment Networks as advisory, consulting, support and coordination bodies of the Institute with the purpose of promoting the training of human resources of academic and professional excellence, as well as the generation of frontier scientific knowledge and its transformation into useful applications for society in these areas.
In January 2009, the Computing Network was created, while in July 2010 the Energy Network was created, adding up to five networks by the end of 2010.
In 2011, the Health and Economic Development Networks were created and for the first time a network of experts was created, in this case, the Telecommunications Experts Network, with the intention of generating technological development.
In September 2011, the "Guidelines for the creation and operation of research and postgraduate networks" were published in the Polytechnic Gazette with extraordinary number 885, which lay the foundations for the organization and operation of all active networks and those in the process of creation.
In June 2012, the Network of Experts in Robotics and Mechatronics is created, having to spend six more years to create two more networks of experts: the Network of Experts in Complex Systems and the Network of Experts in Automotive Innovation, both in September 2018.
In January 2020, shortly before the official start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the **Artificial Intelligence and Data Science Network is created, the latter being the one that integrates the current number of twelve research and postgraduate networks in force at the Institute.
Are characterized by generating cutting-edge knowledge, both in the field of basic and applied science, seeking to transform it into useful applications for society. Likewise, these networks promote the training of human resources of academic and professional excellence that will promote the development of science in the future, with an own polytechnic vision.
Among various topics, alterations to natural resources, both of natural origin (climate change) and anthropogenic, which impact the way of life of the population and their health, with particular emphasis on rural communities and problems of great impact on public health. A fundamental part is the generation of restoration strategies to achieve the reduction of alterations and the generation of healthy ecosystems that allow increasing the quality of life of both human and wild populations.
5 lines of the ENVIRONMENT NETWORK:
-Climate Change -Biodiversity -Water & Soil Pollution -Water Quality and Supplies -Land Use Change

Three main subsectors are distinguished according to the application of biotechnology: medical, agri-food and environmental biotechnology. In the case of agri-food sector, the development of hybrid plants, genetically modified lines resistant to diseases and with superior quality and high-yield seeds, is studied, up to the production of vaccines. These technologies aim to increase the value of food, animals, plants and microorganisms. Agri-food biotechnology can be classified into three large areas: 1) Generation of new plant varieties, 2) Generation of new animal varieties, and 3) Functional foods.
4 lines of BIOTECHNOLOGY NETWORK:
-Molecular Biotechnology -Medical Biotechnology -Environment Biotechnology -Animal Biotechnology
Has focused on developing nanotechnology applied to the health area. Among the research topics developed, we can mention: glucose nanosensors; nanofibers for the incorporation of drugs for the treatment of skin lesions; polymeric nanofibers and composites applied in tissue engineering; Nanomaterials based on nanofibers for drug transport; and tissue engineering in breast cancer. At the same time, the materials area has carried out research that seeks to impact the development of new materials and their applications in energy and the environment.
6 lines of the NANOSCIENCE NETWORK:
-Nanoscience's Fundamental Phenomena -Nano Materials -Micro-Nano Devices & Micro-Nano Systems -Nano-Micro Manufacturing -Instrumentation, Metrology & Standards -Social Impact and Economics of the Micro - Nanotechnologies RNMN

Concentrates its activities in accordance with the great trends in Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) worldwide, these being: AI in everything: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be the most disruptive class of technology on the next 10 years, for its radical computational power, for its application to large amounts of data, and for its advances in deep neural networks. Consideration should be given to: AI, deep learning, cognitive computing, natural language, machine learning, speech user interfaces, autonomous vehicles (airborne, ground, and underwater), intelligent robots, intelligent workspaces. Immersive Experiences: technologies must focus on the activities of the human being, and for this reason they must be much more binding with more adaptable, contextual and fluid technologies within work spaces, at home and in the interaction between companies and people. Consideration should be given to: 4D printing, augmented reality, brain-computer interface, connected home, humans with augmented abilities, nanoelectronics, virtual reality and volumetric displays, medical devices for healthcare. Computer systems with high performance and low energy consumption. Emerging technologies are supported by modern high-performance, low-energy-consumption computing systems, these in turn on intellectual property cores (IP Cores) of semiconductor devices, and the latter vary widely according to the target technology, chips for central processing units (CPUs).
5 lines of the COMPUTING NETWORK :
-Cybersecurity -Mobil Computing -High Performance Computing -Educational Computing and Intelligent Environments

Is aware that the use and supply of energy are essential for the productive activities of society. Its scarcity would result in an obstacle for the development of any economy. Given the decline in oil reserves in Mexico since 2008, generation technologies that use renewable energy sources are required to face the challenges of diversification and energy security. This implies promoting investments and proposing projects that use clean energy. Given this scenario, hydrogen plays an important role as an energy vector, both due to its technical feasibility and its relationship with renewable energies. This fuel, like others, are some of the research topics developed by the EnergyNetwork.
11 lines of the ENERGY NETWORK:
-Alternative Energies (solar, wind, maritime, geothermal, nuclear, etc.) -Bioenergetics Systems -Energetics Efficiency

Has several lines of research that are fundamental axes of the work of the Network, these are: 1.- Chronic-degenerative diseases; 2.- Infectious-contagious diseases; 3.- Perinatal and pregnancy diseases; 4.- Food and nutrition; 5.- Conduct. All these lines are of current importance in health at the national and global level, however the current situation of the COVID-19 pandemic and the latent threats of monkeypox, the resurgence of paralytic polio or the recently described henipavirus infections -Langya, have pointed out the relevance of infectious-contagious diseases in public health problems
5 lines of the HEALTH NETWORK:
-Chronic Degenerative Diseases -Infectious Diseases -Pregnancy and Perinatal Diseases -Food & nutrition -Behavioral Psychology

Is the transition from a specific economic level to a more advanced one, which is achieved through a process of structural transformation of the economic system in the long term, with the efficient allocation of financial resources to support development and equality with the consequent increase in the productive factors available and oriented to their best use, resulting in an equitable growth between the sectors of production. Development implies better living standards for the population, which represents quantitative and qualitative changes, since it is a global process of transformation of a historically determined reality. It intentionally involves the sustainable increase in productive capacities, the increase and better distribution of wealth, attention to the basic needs of the population and the expansion of people's options and capacities for the development of their lives. The dynamics of the Economic Development Network have focused on four areas: a) social and solidarity economy; b) weekly pillars of development; c) identification of PRONACE strategic projects; d) support in technology development activities of other networks
7 lines of the ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT NETWORK:
-Social Organizations & Enterprise Management -Technology & Innovation Management -Innovation towards Integral Education -Economical Growth and Poverty Reduction -Sustainable Regional Development -Marketing & Finances -Cyber systemics

As sub-lines of work are learning for machines and deep training. Through artificial intelligence, it is sought that machines perform tasks similar to those that a human being would perform when making appropriate decisions in uncertain circumstances. On the other hand, through data science, the aim is to develop computational systems that allow decision makers to make informed and relevant decisions. Artificial intelligence and data science are two very important transversal disciplines since at present they impact practically all areas of people's daily lives worldwide. At a national and international level, artificial intelligence and data science are the basis of countless solutions, for example: advisory systems, chatbots, autonomous cars, prediction and control systems.
5 lines of the ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DATA SCIENCES:
-Machine Learning -Artificial Neuronal Networks -Reactive Systems -Rule-Based Systems -Thinking Case Studies

The Expert Networks intend to carry out basic and applied research, generate technological development, provide consultancy and advice on the technological issues they address, and influence the development of regulations and public policies inherent to their subject.
Are currently considered a critical infrastructure of countries. The transition that we are facing as a society towards the so-called digital economy is supported in a very important way by the availability of broadband networks to which the population has access. The countries with the best telecommunications infrastructure obtain a very important advantage to exploit the benefits offered by this new digital economy, which include the migration towards a more efficient operation, both of the private industry and of the government, thanks to the implementation of optimized and automated processes. that use broadband networks and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and Big Data. In the case of Mexico, the levels of Internet access reached a little more than 75% of the population in 2021, so it is necessary to bring services to those people who are not connected and offer them the possibilities of economic and social development that they could have. at their fingertips once they have access to the Internet.
10 lines of the TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK:
-Communication Systems -Modeling of Propagation and Antennas -Hardware-Software for Telecommunications -Electromagnetic Compatibilization into the Communication Systems -Signal Processing -Nanotechnology for Telecommunications -Data, Audio & Video Networks -App Development for Communications/ Remote Sensing Technology -Aerospatiale Telecom

Is currently working on "Education for Robotics and Mechatronics", with the aim of building collaboration bridges between all members of the network (higher secondary, higher and postgraduate level). The impact and potential at a national and international level that this research has lies in proposing and exploring how robotics and mechatronics can affect the educational field, through the creation of tools and methodologies. That is to say, through the realization of educational and academic projects where the teaching and learning of robotics and mechatronics can be the object of study, or engineering projects where mechatronics and robotics can be the means by which They can develop tools, systems, products or processes that favor the teaching and learning of science.
8 lines of the ROBOTICS AND MECHATRONICS NETWORK:
-Design of Robotic & Mechatronic Systems -Applied Intelligent Systems -Control and Automation Systems -Manufacturing Systems -Robotic & Mechatronic for Medical Applications -Artificial Vision Systems -Virtual Reality and Haptic Interfaces -Autonomous Mobile Vehicles

Have emerged in recent years as a tool to understand processes whose study cannot be reduced to that of their components. Its development has given rise to the constitution of working groups in the world's major research centers that apply the theory of complex systems to the search for solutions in very different fields of knowledge. Complex systems are systems composed of multiple states, where the states can be compound or individual and the simultaneous interaction between them is capable of producing emergent behaviors and these cannot be inferred until the system evolves. Complex systems evolve in non-linear and non-centralized media, within their emerging behaviors it can be observed: self-organized, self-adaptive, and critical, chaotic or oscillating patterns.
4 lines of the COMPLEX SYSTEMS NETWORK:
-Complexity, Time-Series & Fractals -Complex Systems Applied to Social and Economic Systems -Socio-Spatial Complexity: Territory, Cities, -Architecture and Habitability
Is to promote the actions and programs of the Institute aimed at the formation of specialized human capital, scientific and technological development, as well as the appropriation of knowledge of new sustainable transportation technologies that promote the technological autonomy of the automotive section. Its vision is to be a transdisciplinary organization, recognized by the automotive sector as a reliable provider of frontier and sustainable technological solutions, as well as a benchmark in the establishment of technical standards and public policies related to new vehicle technologies.
3 lines of the AUTOMOTIVE INNOVATION:
-Electrification of Transport -Transitional Technologies towards Electrification -Autonomous and Semi-autonomous Transportation

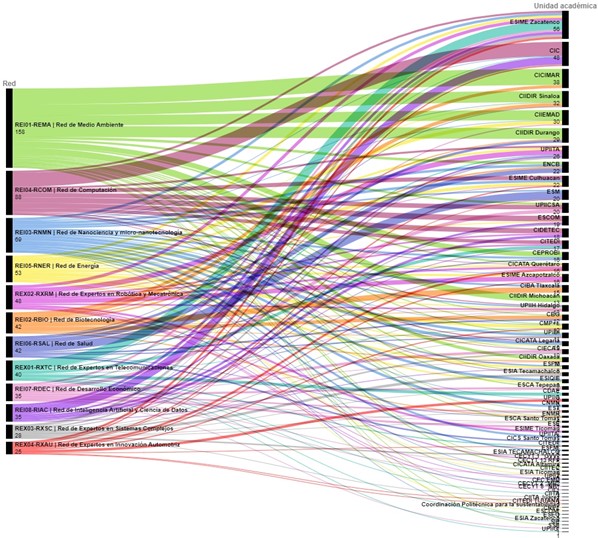
As of January 2022, 728 active members were registered. The academic unit that contributes the largest number of members to the networks is ESIME Zacatenco, with 56 members distributed in 9 of the networks, followed by CIC, which contributes 48 members in five networks, although in two networks it is a single individual. At the other extreme, the network with the lowest number of members is the Network of Experts in Automotive Innovation, with only 25 members. The group of polytechnic entities includes academic units of Higher Secondary and Higher Education, Research Centers, Liaison Centers, and bodies such as the Secretariat of Research and Graduate Studies.
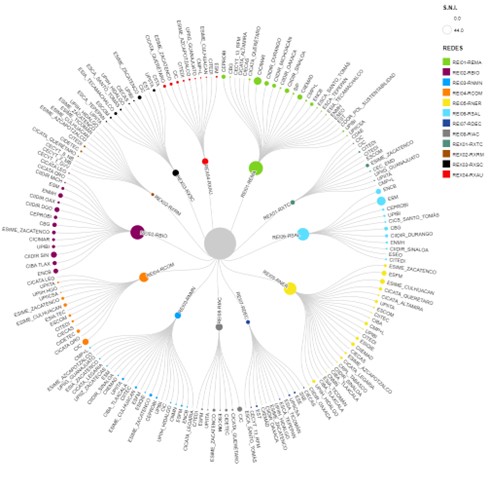
In relation to the number of professors recognized in the Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (SNI, by its acronym in Spanish), based on the number of members registered in the networks, out of 816 members registered in the networks, 479 researchers belong to However, looking closely at each of the networks, it can be seen that the Biotechnology Network has 85% of its members registered in the System, while the Robotics and Mechatronics Experts Network has only 9% of SNI researchers. This is explained by the type of activities they develop, several of them linked to the application and development of technology (rather than science).